Viruses vs. Bacteria: Key Differences Explained
Discover how viruses differ from bacteria in structure, function, and treatment. Learn why these differences matter for health.
How Are Viruses Different from Bacteria? Understanding the Key Differences
When it comes to microorganisms, viruses and bacteria are the two most commonly discussed entities. While both can cause infections and have an impact on our health, they are fundamentally different in many ways. Understanding these differences is crucial not only for scientific knowledge but also for effective medical treatment and prevention strategies. In this article, we will delve into the key distinctions between viruses and bacteria, providing you with a clearer picture of these microscopic life forms.
What Exactly Are Viruses and Bacteria?
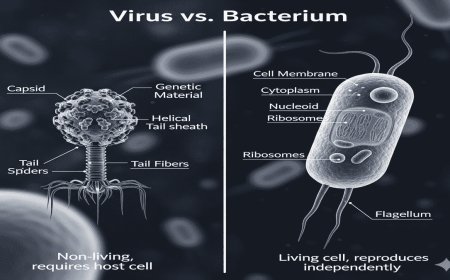
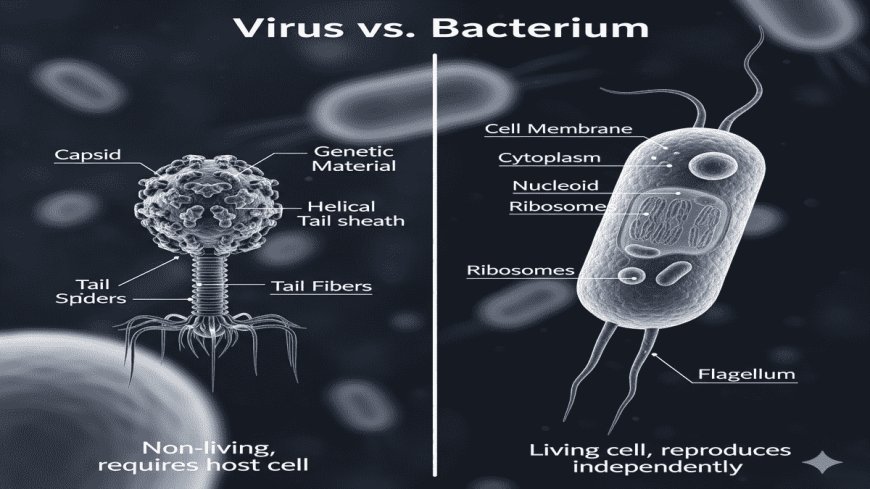
Before we dive into the differences, it’s essential to define what viruses and bacteria are. Viruses are tiny infectious agents that can only replicate inside the living cells of an organism. They are composed of genetic material, either DNA or RNA, encapsulated within a protein coat, and sometimes surrounded by a lipid envelope. Viruses are not considered living organisms because they cannot carry out any metabolic processes on their own.
Bacteria, on the other hand, are single-celled microorganisms that have a more complex cell structure. They are considered living organisms because they can reproduce independently, metabolize nutrients, and perform cellular processes. Bacteria come in various shapes and sizes, and while some cause diseases, many play beneficial roles in ecosystems and human health.
Structural Differences
Size and Complexity
One of the most apparent differences between viruses and bacteria is their size. Viruses are much smaller than bacteria, often measuring just a few nanometers in diameter, whereas bacteria can be up to several micrometers in size. This size difference is significant enough that bacteria can often be seen with a regular light microscope, while viruses typically require electron microscopy for visualization.
Cellular Structure
Bacteria have a more complex cellular structure compared to viruses. They possess a cell wall, cell membrane, cytoplasm, and various organelles necessary for life processes, such as ribosomes for protein synthesis. Conversely, viruses lack these structures entirely. They are mere packets of genetic material that rely on a host cell’s machinery to replicate.
Reproduction and Life Cycle
Bacteria reproduce independently through a process called binary fission, where a single bacterial cell divides into two identical cells. This ability to reproduce on their own allows bacterial populations to grow rapidly under favorable conditions.
Viruses, incapable of reproducing on their own, must infect a host cell to replicate. Once inside, they hijack the host’s cellular machinery to produce new virus particles, often damaging or destroying the host cell in the process.
Treatment and Resistance
The differences in structure and replication also impact how infections caused by viruses and bacteria are treated. Bacterial infections are typically treated with antibiotics, which target specific bacterial structures or functions. However, antibiotics are ineffective against viruses because viruses lack these structures.
Viral infections often require antiviral medications, which work by interfering with the viral life cycle. Vaccines are also a critical tool in preventing viral infections by priming the immune system to recognize and attack specific viruses.
Real-World Examples
Understanding the practical implications of these differences can be seen in real-world scenarios. For instance, the common cold and flu are caused by viruses, while strep throat and urinary tract infections are bacterial. Misuse of antibiotics for viral infections can lead to antibiotic resistance, a growing concern in global health.
Conclusion: Why These Differences Matter
Recognizing the distinctions between viruses and bacteria can help us make informed decisions about treatment and prevention. It highlights the importance of correct diagnosis and appropriate use of medications. By understanding these microscopic entities better, we can improve our health responses and prevent the spread of infections more effectively.
If you found this information helpful, consider sharing it with others to spread awareness about the crucial differences between viruses and bacteria. Knowledge is power, and understanding these differences can lead to better health outcomes for everyone.
What's Your Reaction?
 Like
0
Like
0
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0